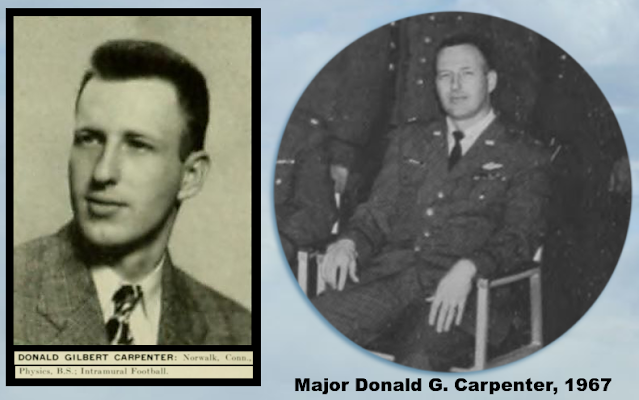
Controversy erupted with the disclosure that UFOs and aliens were the subject of a textbook at an accredited four-year university, the United States Air Force Academy. The publicity caused the US government great embarrassment, and news stories subsequently reported that the textbook was withdrawn, the UFO studies canceled. The facts are now in, and the real story can be told, including how the author of the book went on to explore eternal youth, ghosts, and measuring the mass of paranormal entities and human souls.
There are three main sections to this virtual booklet:
- The Textbook… and The UFO Scandal
- The UFO Chapter, an Official Disclosure?
- Professor Carpenter’s Path to the Paranormal Afterwards, documents and references:
- PDF of the 3 USAFA Textbook UFO Chapter Versions and Related Documents
- Acknowledgements, Sources, and Resources
- Donald G. Carpenter’s Published Works
Join us now in the history of another one of…
The Textbook
Donald Gilbert Carpenter went to college, joined the Air Force, earned a Ph.D. in Physics, then became a professor for the United States Air Force Academy (USAFA or AFA). Carpenter worked under Colonel Anthony J. Mione, who became the head and first permanent professor of the physics department at the USFA in 1966.
Under Mione’s watch in 1968, the Academy taught a course for third-year cadets, Physics 370, using Introductory Space Science, the textbook edited by Major Donald G. Carpenter. The book’s 33 chapters were written by Carpenter and other Air Force experts, published for the course’s 1968 Fall semester. As later described by the Air Force, it was “a 470-page textbook printed by the AFA, [it] is used by approximately 20 cadets each semester who are enrolled in Physics 370, a small elective course.” The AFA reportedly printed 200 copies, to be used exclusively by the class. The book consisted of two spiral-bound volumes with a total of thirty-three chapters. It was the final section that caused a news flap when the word got out, “Chapter XXXIII Unidentified Flying Objects.”
Why was the UFO topic included in the Air Force’s Physics class on space science? The introduction only indicated it was a problem:
“The literature on UFO's is so vast… we can only present a sketchy outline of the subject… [including] description classifications, operational domains (temporal and spatial), some theories as to the nature of the UFO phenomenon, human reactions, attempts to attack the problem scientifically, and some tentative conclusions.”
The Air Force traditionally discussed UFOs in terms of mistaken identification, but Carpenter spent only about a sentence on that, saying instead, “What we will do here is to present evidence that UFOs are a global phenomenon which may have persisted for many thousands of years.” There was little in the 14-page chapter about how UFOs might relate to concepts of propulsion or space travel, but it said our laws of physics might not apply. “We should not deny the possibility of alien control of UFOs on the basis of preconceived notions…” Carpenter briefly discussed aspects of reported UFO and alien encounters, lingering on the 1957 attack on the Sutton family near Kelly, KY, the 1964 Lonnie Zamora incident, and the 1961 abduction story of Barney and Betty Hill. While Carpenter attempted to be balanced, the reader was left a bit whipsawed:
“The entire phenomenon could be psychological in nature but that is quite doubtful... The phenomenon could also be entirely due to known and unknown phenomena (with some psychological ‘noise’ added in) but that too is questionable in view of some of the available data. This leaves us with the unpleasant possibility of alien visitors to our planet… three and maybe four different groups of aliens… A solution to the UFO problem may be obtained by the long and diligent effort…However, even if such an effort were made, there is no guarantee of success… there may be nothing to find…”(We will continue the examination of the contents of the chapter in another section.)
Following Carpenter’s conclusion, he presented a list of 18 books and articles on UFOs, references “to read further in this area.”
The Academy used Carpenter’s textbook through the Fall and Spring 1968-69 and 1969-70 semesters. Shortly after the 1970 semester began, national media carried the news that the Air Force was teaching its cadets about UFOs and aliens.
The UFO Scandal
The Aerial Phenomena Research Organization’s APRO Bulletin May-June 1970, was aware of the USAFA textbook, saying it had “caused quite a stir in UFO circles in the first half of 1970.” That was nothing compared to the stir that came a few months later when, thanks to ufologist Earl J. Neff, the tabloid press got a hold of the story in late September. The National Enquirer dated Oct. 11, 1970, carried a cover headline breaking the news, and the opening line stated:
"A textbook used by the Air Force Academy to teach cadets warns them that Unidentified Flying Objects (UFOs) could be real spacecraft operated by alien peoples who are closely watching the world.”
The mainstream press subsequently picked up the story and it was covered widely in newspapers:
 |
| Miami Herald, Omaha World-Herald, Seattle Post-Intelligencer, UPI, Oct. 1-2, 1970 |
Lawrence Fawcett and Barry J. Greenwood discussed the 1970 textbook drama in pages 13-14 of their 1984 book, Clear Intent: The Government Coverup of the UFO Experience:
“The whole [UFO] section came as something of a jolt to outsiders. Here was a very clear admission that UFOs were a difficult problem and warranted extensive scientific study. And this was being taught to Air Force cadets! It made the entire Blue Book effort seem rather hollow and unsubstantial.”
The National Investigations Committee on Aerial Phenomena (NICAP) said in their UFO Investigator, Oct. 1970, “NICAP obtained a copy of the textbook's UFO chapter in October 1969. No attempt was made to publicize it…” The author had spoken to Carpenter and obtained a rare quote; introducing it, NICAP said:
“The chapter was written in 1968 by Major (now Lt. Colonel) Donald G. Carpenter… at the request of his superiors, who wanted to update educational material being used by the Physics Department, Carpenter was under no obligation to seek clearance work from the Pentagon or other high Air Force office. He did submit the textbook to the Academy’s public information office, but no objection was raised to the UFO chapter.
In speaking recently with Carpenter (who no longer teaches at the Academy), NICAP asked his personal opinion on the subject of UFOs. ‘I have no firm conclusions,’ he said; ‘I can see merit in more than one point of view, and I find the data exceedingly interesting.’ He went on to explain that his purpose in preparing the UFO chapter was not to stress one hypothesis or take a particular position, but to give the students an overview of the problem.”
The New Chapter 33: U.A.P.
NICAP’s UFO Investigator, Dec. 1970, reported:
“Air Academy Replaces UFO Text: Switch Comes After Fuss Over Old Version.”
NICAP suspected a cover-up. At the time of the news blitz, the USAFA instructor of Physics 370, “Captain Edward Peterson offered to send an ‘Errata and Addenda’ sheet to NICAP to show how the UFO section had been updated, not replaced.” However, “Following widespread news stories that played up the text’s liberal treatment of the UFO controversy, the Academy substituted a much abbreviated, ‘revised’ version of the 14-page textbook chapter, contending that the old version was ‘out of date’…” NICAP identified Capt. Peterson as the author of the new chapter, and acknowledged that “the revised text retains a large measure of the objectivity of the old chapter.”
A more thorough official explanation of the chapter replacement came from Col. James F Sunderman, USAF, Director of Information, Nov. 4, 1970:
“In light of [recent] developments, the in-class content of the course was changed to present orally the conclusions of the Condon report and the reasons why the Air Force cancelled Project Blue Book. It was considered uneconomical to reprint the entire second volume for such a limited number of students until the fall of 1970. Beginning with the 1970 fall semester, a revised updated chapter entitled 'Unidentified Aerial Phenomena’ has been substituted for the old chapter so that the text now follows the oral in-class presentation on this subject.”Captain Edward A. Peterson’s new 7-page chapter, “Unidentified Aerial Phenomena” also favored the extraterrestrial hypothesis for UFOs, but it attempted to be a balanced overview, concluding in part:
“Based on the conclusions of the Condon report and its own twenty-year UFO experience, the Air Force terminated Project Blue Book… Criticisms of the Condon report include the contention that the conclusions reached are not supported by the bulk of the evidence in the report itself and that the firing of two staff members for ‘incompetence’ before the completion of the final report raises questions concerning the objectivity and completeness of the study.
…It is unlikely that any new official scientific studies will be forthcoming... The UFO problem must now compete on its scientific merit with all the other pressing scientific problems facing mankind.”
That was supposedly the end of it. Most people thought the Air Force Academy stopped teaching about UFOs. Not so.
1972: The UFO Mystery
The extent that Donald Carpenter corresponded with ufologists is largely undocumented, but the archives of prominent Canadian researcher Arthur Bray contain an item believed to be from 1968: “an unpublished chapter entitled ‘Unidentified Flying Objects’ from the book ‘Introductory Space Science: Volume II’. The chapter was sent to Arthur Bray and signed by the author.”
In 1970, Maj. Carpenter made a complete revision of his original chapter 33, preserving the original tone, but reordered, corrected, and updated. It also incorporated data from the 7-page Fall 1970 semester substitute by Capt. Peterson. Copies of the 28-page manuscript were privately circulated, and one reached the hands of Dord Fitz, a traveling art teacher with an interest in the paranormal.
In 1972, Environmental Space Sciences was published in Northbrook, Illinois, by Whitehall Company, a revised version of Carpenter’s 1968 textbook. In the acknowledgment section, Carpenter thanked those who had helped him, including Captain Edward A. Peterson, and said, “strong encouragement was offered by Col. Anthony J. Mione, Permanent Professor of Physics at the United States Air Force Academy.”
Instead of excising the UFO material, instead it was given greater prominence. The back cover stated, “This book provides some of the essential information needed… [for] the whole new and fascinating field of Space Science, including the problem of the UFO.” The title of the revised 26-page chapter 33 was “The UFO Mystery.”
The UFO chapter’s list of references grew from the original 18 to 23, adding:
- Scientific Study of Unidentified Flying Objects by Dr. E. U. Condon, 1969.
- “More on UFOs,” a letter by Stanton Friedman, Physics Today. January 1971.
- UFOs? Yes! by David Saunders and Roger Harkins,1969.
- “UFOs: Greatest Scientific Problem of Our Times?”, paper by James McDonald, 1967.
- Flying Saucers: Hoax or Reality? by Jerome Stanton, 1966.
Carpenter discussed several UFO cases as before, but he dropped the sketchy unverified tale of two sentries burned by a UFO on Nov. 4, 1957, at Fort Itaipu, Brazil. He again presented the “Book of Dzyan” story, but as an example of the misinformation so often found in UFO lore.
“The reason for including this hoax at this point in this chapter is to show you, in a way that you will remember, that just because someone tells you that something is true does not make it really true. You must be skeptical of all information presented both by UFO buffs and UFO detractors. As of right now there is no conclusive evidence for either side.”
In the section, “Medium Scale Scientific Efforts,” Carpenter discussed the flaws in the Condon UFO Study and said, “The Condon Report conclusions may well be correct . . . but they may also be quite wrong.” He retained the closing of the original chapter 33, advising readers to “to keep an open and skeptical mind.”
The full text of the original manuscript of “The UFO Mystery” and the version published in the textbook are both included in our PDF at the end of this article, without omissions or embellishments, for the first time since the 1970s.
Environmental Space Sciences was published for use as a textbook by schools and colleges, and the magazine The Science Teacher, Nov. 1973, carried a review of it.
How many educational institutions used Environmental Space Sciences is difficult to determine, but there was an important one. The United States Air Force Academy purchased it for Physics 370, and just like magic, there was a UFO chapter back in their textbook, but this time carried a disclaimer. “This book is not a United States Government publication.”
ESS flew under the radar and escaped a new media storm. However, the press was still churning the old story.
An erroneous story on the old textbook surfaced in the tabloid Midnight, Nov. 5, 1973:
“The US Air Force Academy has withdrawn from use a textbook which warns cadets of the existence of Unidentified Flying Objects, apparently because of fears that the textbook's contents would become public knowledge.” Later it said, “MIDNIGHT's UFO expert, Hayden Hewes, says that despite all the solid information contained in the textbook, the Air Force decided to withdraw it from classroom use when word of the book's existence began to leak out to the public.”(The tabloids revived the story every few years, as if it were a new discovery.)
Col. Mione's support of UFO Studies
Asked about the Air Force Academy’s textbook chapter on UFOs, on December 13, 1973, Col. Anthony J. Mione, wrote back to William Gordon Allen, saying they were still teaching the topic as part of Physics 370:
“As a general response, we are continuing to present essentially the same material covered in the draft that you have. However, we now use the commercially published version Environmental Space Sciences published by the Whitehall Company… In this text an expanded section on UFOs and extraterrestrial life is included. The section attempts to provide a hopefully unbiased summary of UFO information and concludes, ’the best thing to do is to keep an open and skeptical mind and not take an extreme position on any side of the question.’
To further expand on the background we hope our graduates will have, we invited and had Dr. Stanton Friedman visit with us last April. During his visit he presented two large audience lectures and two seminars essentially in support of his subject, ‘Flying Saucers are Real.’
I hope you gathered that we do make a continuing and real effort to provide our students with all views of current topics. They are expected to come to their own mature conclusions based upon the broadest foundation of knowledge and information that we can provide.
Yours truly, Anthony J. Mione, Colonel, USAF,
Professor and Head (of the Department of Physics)”
William Gordon Allen reproduced the letter in his 1974 book, Overlords and Olympians, and featured it in his rather imaginative documentary, Overlords of the UFO, 1976. (Virtually everything from Allen besides the text of the letter from Col. Mione should be disregarded.) Here’s a clip from Overlords of the UFO with the section on the USAFA and Col. Mione’s letter. 1977-03-08: UFO Col Anthony J Mione.
Col. Mione mentioned ufologist (not Dr.) Stanton Friedman lecturing for his cadets. We couldn’t find any documentation on that, but Friedman was lecturing about 120 miles away at Colorado State University on April 19, 1973, so he was close enough to speak at the Academy as well that month.
 |
| Fort Collins Coloradoan, April 19, 1973 |
In the National Enquirer article, March 14, 1978, “Air Force Academy has One of Largest UFO Libraries,” by Charles Cobb, Col. Mione said that the USAFA used Carpenter’s revised textbook in the Physics 370 course from 1972 until 1974. The article also mentioned an incident from the chapter, an F-86 jet firing on a saucer. “The book, "Environmental Space Sciences" edited by retired Air Force Col. Donald Carpenter does not disclose where and when the encounter took place. Carpenter, now of North Granby, Conn., told The ENQUIRER that he no longer has the documents that would enable him to pinpoint the location and date of the incident. Carpenter once taught the space science course, which was replaced by an astronomy course in 1974.”
(The source for the F-86 story will be resolved in our next section.)
It seems no one paid any attention, but at least twice, Col. Mione disclosed that the UFO subject had continued to be taught to Air Force cadets. We asked US Air Force Academy Research Librarian Joseph Barry, who provided confirmation by email:
“For Fall 1972 the Department of Physics used the updated and retitled textbook [Environmental Space Sciences] by Lt Col Donald C. Carpenter for Physics 370. They ordered 50 copies for that semester with delivery from the Whitehall Company. Volume I of older edited edition by Carpenter, Introductory Space Science (two volumes) was still made available for the Fall 1972 semester because the Department of Physics did not have it in sufficient quantities. I believe the text Introductory Space Science (Vol I and II) was published in 1966 but reprinted and updated in 1968. By Fall 1974 semester, a new text was selected to replace Space Environmental Sciences entitled Astronomy Fundamentals and Frontiers by Jastrow and Thompson.”
The Air Force estimated “approximately 20 cadets each semester” for Physics 370, and with the Fall and Spring sessions from the 1968-9 to 1973-4, that would equal at least 240 students enrolled. The United States Air Force Academy’s Physics 370 included UFOs in their studies for at least six years.
The UFO Chapter, an Official Disclosure?
The Air Force Academy textbook’s chapter 33 was an overview of the UFO topic and attempted to present a balanced view of the topic, but… Looking at Carpenter’s references/bibliography for the chapter, we can see he was drawing from some shaky sources, mostly flying saucer books from the popular press. As a result, he repeated some far-out speculative notions from them, unwittingly including some hoaxes and tall tales as if genuine.
Carpenter used Frank Edwards Flying Saucers - Serious Business, 1966 as a source, and from it he pulled a several bits, including an ancient legend recounted from “the Book of Dzyan,” about a flying huge shining metal vessel that unleashed fire on a city, and burned and blinded the people below. From it also came the story of Alexander Hamilton, who swore a strange cigar-shaped flying machine had stolen his cow. For the 1972 book, Carpenter corrected the Book of Dzyan gaffe, but it wouldn’t be until the mid-1970s that the cow hoax was straightened out. Jacques Vallee had brought the Alexander Hamilton cow-knapping story into UFO lore in Anatomy of a Phenomenon, 1965, and it was widely circulated as genuine until 1976/7 when researchers received testimony and uncovered Hamilton’s old confession of the hoax. (Jerome Clarke’s Extraordinary Encounters: An Encyclopedia of Extraterrestrials and Otherworldly Beings, 2000.)
 |
| From the cover illustration: Flying Saucers and the U.S. Air Force by Lawrence J. Tacker. |
One of the most dramatic parts of Carpenter’s chapter was the story of a US military encounter with a saucer-shaped UFO:
“About ten o'clock one morning, a radar site near a fighter base picked up a UFO doing 700 mph… two F-86's were scrambled to intercept. …The UFO began to accelerate away but... the pilot armed his guns and fired… the UFO pulled away rapidly, vanishing in the distance.”
The tale was neither a new disclosure, nor even secret. It was originally featured in the very first line of the 1956 book, The Report on Unidentified Flying Objects, by Captain Edward Ruppelt:
“In the summer of 1952 a United States Air Force F-86 jet interceptor shot at a flying saucer.”
Several months before the textbook story went viral, the APRO Bulletin May-June 1970, said that the excitement of ufologists was unwarranted, because the material published was not “of an official nature,” and it leaned “heavily on published material from the field of civilian UFO research and reach[ed] no conclusions.”
APRO got it right, but few paid any attention. The chapter was not drawn from original UFO data or investigations, it was written without any input from Project Blue Book. Carpenter made a good faith attempt to survey the body of knowledge on UFOs. His mistake was including material from books written by some careless and imaginative authors in the popular press.
The most sensational aspect of the story was Carpenter’s discussion of aliens, whom he suggested might come from civilizations on our neighboring planets.
“…what questionable data there are suggest the existence of at least three and maybe four different groups of aliens... It implies the existence of intelligent life on a majority of the planets in our solar system, or a surprisingly strong interest in Earth by members of other solar systems.”
Carpenter listed four types of commonly described aliens (paraphrasing):
1. Little men, 3.5 feet tall, with a round head, long arms, wearing space suits/coveralls.2. A humanlike species.
3. The Hill’s species, short with wrap around eyes, and mouths with very thin lips.
4. Hairy dwarves, about four feet tall, covered with thick hair or fur.
 |
| The Aliens by Hayden Hewes, 1970. Illustrated by Hal Crawford. |
A few years later, Ufologist Hayden Hewes’ article, “Alien Coincidence?” in Flying Saucers: Mysteries of the Space Age, June 1976, noted that the textbook appeared seven months after the publication of Hewes's booklet The Aliens, which contained similar (illustrated) descriptions of four alien species. Carpenter and Hewes may have just been reading the same speculative 1960s literature on alien species.
Speaking of unreliable sources, repetition of old tales can cause a misinformation loop. In late 1973, Donald Keyhoe’s final UFO book was published, Aliens from Space: The Real Story of Unidentified Flying Objects. Throughout it, Keyhoe repeatedly cited and quoted from Introductory Space Science chapter 33 as if it contained genuine disclosures and, “damaging admissions” from the U.S. government. Keyhoe was proud that his own books were cited as chapter 33 sources, but he failed to realize that it showed Carpenter was merely summarizing concepts and tales from UFO literature.
Fortean author John Keel gave a savage review of Keyhoe’s book (and Carpenter’s chapter 13) in Caveat Emptor, March-April, 1974.
“Aliens From Space is primarily a paste-up job, many sections lifted intact from the pages of NICAP's newsletter… There are a great many distortions of fact, some of them apparently deliberate; and tragic omissions… He even drags in the Book of Dzyan, by quoting the celebrated Air Force Academy UFO text which, incidentally, was composed by a flying saucer zealot and did not represent that agency's position at all. The Book of Dzyan is not an ancient document but was composed by dear old Madame Blavatsky in the 19th century. Keyhoe just quotes the AF Academy rubbish which, he must have known, was lifted almost entirely from Frank Edwards.”
Donald Keyhoe apparently thought that having the Air Force publish bogus stories in a textbook made them authentic, and he repeated them without research or verification. Keyhoe was just one of many ufologists who recirculated Carpenter’s UFO chapter as proof of the Air Force’s cover-up about their true knowledge of extraterrestrials and their spacecraft. Generations since have carried on the tradition.
Professor Carpenter’s Path to the Paranormal
Donald G. Carpenter was born in Connecticut on May 23, 1927. The timeline of his military career and education below is based on Who's Who in the West for 1972 and contemporary media reports. Carpenter served in the Navy as Seaman 1st Class in World War II, and afterwards began his college education.
1951: B.S. degree in physics in 1951 from the University of Maryland.
1952-54: Electronic design at Kirtland AFB, New Mexico.
1955-62: A senior pilot at Otis AFB, MA, Wright-Patterson AFB, OH, and Offutt AFB, NE.
1960: M.S. degree in nuclear engineering from the Air Force Institute of Technology.
1962: Ph.D., Physics, Iowa State University of Science and Technology.
1962-67: Became an associate professor of physics at the US Air Force Academy.
1967-68: Research associate professor, USAFA.
1968-69: Head of Environmental Science Div.
1969-71: Space systems analysis with the 14th Aerospace Force, Ent AFB, Colo.
1971-72: Commander of the 16th Surveillance Squadron at Shemya AFB, Alaska.
The Shemya AFB stint was for Spacetrack, to provide space object cataloging and identification, “an integrated worldwide single manager system, and represents Headquarters USAF as the operational planning agency for space surveillance.”
Through the years, Carpenter’s progress earned him advancements in rank from Captain to Lt. Colonel. In the fall of 1972 Carpenter received a prestigious award for his work, as reported in Aviation Week & Space Technology. At the Air Force Association’s annual National Convention on Sept. 17, 1972:
“Donald G. Carpenter has received the Theodore Von Karman Award for Science and Engineering in recognition of his contribution to the Air Force and the nation for ‘advancing the nation's space defense capability.’ While stationed with the 14th Aerospace Force, Col. Carpenter isolated a major cause of error bias of position calculation of satellites; from this he formulated a radically new and fundamental theory of specific space environmental effects that improved Spacetrack accuracy by a factor of ten.”
By this time Carpenter had served in the Air Force for over 20 years. In 1977, Carpenter had retired from the USAF, and was seeking permission from Congress to teach abroad.
That covers Carpenter’s military career, but rewinding a bit, let’s look at what else he was working on. We can’t document the origins or depth of Carpenter’s interest in UFOs, but it would have been impossible for him to serve in the Air Force at Wright-Patterson without some familiarity in the topic. His 1962 dissertation on ball lightning for his Ph.D. could be considered UFO-related, and one of his references was "Theory of the Lightning Balls and Its Application to the Atmospheric Phenomenon Called 'Flying Saucers'", Carl Benedicks: Arkiv for Geofysik (Sweden), vol. 2, p. 1, 1954. The sources and references cited for his UFO chapter and its update show that he became very familiar with the topic and followed it closely at least up until the early 1970s.
While working on his B.S. at Wright-Patterson AFB, "In late 1959, Dr. Donald G. Carpenter deduced the theory [of extending the human lifespan] from studies of nuclear science and radiation effects." Designing the Future: The Role of Technological Forecasting by Robert W. Prehoda, 1967.
Carpenter’s 1967 letter to Science magazine on human longevity:
“The story of Adam and Eve explains that mankind lost eternal youth through original sin, and stories of arrangements with the devil (Dr. Faustus) point the moral that the search for eternal youth is evil… Yet considerable prestige would accrue to the country that first bestows extended youth upon the rest of the world, and [it] would permit an increased rate of scientific and economic progress.”
In 1969 Carpenter wrote a scientific paper relating to youth extension, “Biological Aging as a Diffusion Phenomenon” in Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 31, 487–504. Aerospace Medicine and Biology. Jan.-Jun. 1970, included it in their bibliography of “references to unclassified report and journal articles that were introduced into the NASA scientific and technical information system during January, 1970.”
Carpenter was a reader of Analog Science Fiction and wrote several articles and letters of comment to the magazine over several decades. His article with Captain John E. Wrobel, Jr. Department of Physics, Air Force Academy) appeared in Analog, Dec. 1969, “Is Biological Aging Inevitable?”
Two years later, the topic was still on his mind, and Carpenter lectured on “Extended Life” for the Ent AFB Officers’ Wives Club (Colorado Springs Gazette-Telegraph, April 9, 1971.) Then in 1971, he spoke about longevity at a conference, receiving national media attention.
Carpenter tried his hand at science fiction, in 1973 self-publishing via Vantage Press the novel The Treacherous Time Machine under the pseudonym “Merlin Mesmer Merlino.” Written for young readers, it’s described by Goodreads as “An adventurous journey backward in time to Germany in the year 1227 A.D.”
We were unable to locate a copy of the novel anywhere, but the McDermott Library at the U.S. Air Force Academy in Colorado has one.
After Col. Carpenter’s retirement from the Air Force, he stopped referring to his rank in print and identified himself as Dr. Donald Gilbert Carpenter. It was then that he began writing about ghosts, souls, and paranormal entities.
 |
| As reprinted in Thailand |
Analog Science Fiction, Oct. 1980 featured Carpenter’s essay, “The Physics of Haunting,” which listed the seven phenomena of ghosts beginning with:
“1. The theory believes that ghosts only appear at night. And each appearance occurs only a few seconds before fading away. 2. A ghost or spirit can glow. And will have the brightness equivalent to 1-20 lux, which is the intensity level that the human eye can see.”
 |
| New York Times, March 11, 1907 |
In 1984, Carpenter’s “Weighing the soul at death: Some methodological and theoretical considerations” was published in Theta, Journal of Psychical Research 12, 14–16. Carpenter also discussed ghosts, suggesting that the energy required for a ghost to function is limited to around 60 Joules based on anecdotal reports.
From 1990 to 1994, Carpenter listed himself as being associated with the Department of Electrical Engineering, Colorado Tech. In 2000, he mentioned no affiliations, just gave his personal information and the email, "TheTopProf@msn.com." See the appendix below for his scientific papers, and other writings, which include his work up into the 2000s.
In 1998, Donald Gilbert Carpenter published an e-book, Physically Weighing the Soul. One reader of his book said, “I especially like Carpenter's reminder that souls aren't the only spiritual beings thought to inhabit bodies. And some of the others might be messing around with the experiment.”
Carpenter wrote about the soul masses of different animals and entities. Studying them, he concluded, "This makes me suspect that Leprechauns… are most likely discarnate humans." (As quoted by Mary Roach in Spook: Science Tackles the Afterlife, 2005.)
The Final Chapter
Dr. Carpenter’s last documented activity was UFO-related. George Filer published an incomplete reprint of the 1972 chapter.
“Environmental Space Sciences is a book taught at the Air Force Academy… Col. Carpenter was kind enough to send Eastern MUFON the book he edited and wrote with six other officers. Most of the book pertains to science of space, the sun, planets, plasmas, magnetic fields, radiation, meteors, planets, space dust, Cosmo chemistry, the planets and moons... All the chapters are of interest to the Ufologist, such as the Search for Extraterrestrial Life, but most important is: Chapter XXXIII, The UFO Mystery.”
Colonel Anthony J. Mione supported Carpenter teaching the UFO material at the USAFA, and without him, it would have never happened. Col. Mione died on May 15, 2009, at the age of 82.
 |
| Donald Gilbert Carpenter 1927- 2011 |
We were unable to locate an obituary for Donald G. Carpenter, but documentation shows that he last lived in El Paso, Colorado, died on March 27, 2011, and received a military burial. His headstone shows he received the Legion of Merit and the Meritorious Service Medal. The Social Security Death Index lists some further details about his military service and final resting place:
“Carpenter, Donald G., Rank: S1C, COL, Branch: US NAVY, US AIR FORCE, War: WORLD WAR II, KOREA, VIETNAM, was born 23 May 1927, died 27 March 2011, and was buried in Section 30B, Site 149 in Ft. Logan National Cemetery in Denver, Colorado, U.S.A.”
The UFO chapter in Dr. Carpenter’s textbook has become the subject of much everlasting speculation and controversy. Donald G. Carpenter made a sincere effort to present the complexity of UFO topic to students based on the best available knowledge at the time. He earned the right to be remembered for that.
The Three UFO Chapter Versions and Related Documents
Below is a link to a 94-page PDF of correspondence from the Air Force on the USFA Academy’s teaching of the UFO subject, and their release of the first two versions of chapter 33. It’s followed by Donald G. Carpenter’s 1970 manuscript, the 1972 book chapter, and then three related articles.
PDF of the 3 USAFA UFO Chapter Versions and Related Documents
. . .
Acknowledgements, Sources, and Resources
Thanks to Barry Greenwood and Isaac Koi for Air Force documents and correspondence. Isaac Koi’s entry for the USAF Academy textbook article includes a list of books discussing Carpenter’s UFO chapter.
TK at Kook Science provided career and biographical details on Donald G. Carpenter.
Some of the additional data for this article was located with tips from Reddit contributor “ithinkwithink” who gathered information on Carpenter and his other USAFA textbook coauthors.
Some of Carpenter’s scientific papers were located from data from Natural Philosophers Wikipedia.
The Natural Philosophy Database (formally WorldSci.org) a “catalogue [of] all dissident science work,” has an entry on Donald G. Carpenter and his papers and conferences attended.
The USAF response to MUFON’s inquiries about the USAFA Physics 370 textbook, “John Schuessler Gets Prompt Reply from the Air Force,” Skylook, December 1970, pg. 4.
Confirmation of Carpenter’s military career and education came in part from Polaris, the yearbook for the US Air Force Academy.
US Air Force Academy catalogs circa 1955- 1986 are archived by the HathiTrust Digital Library.
The text of both the 1968 and 1970 versions of Chapter 33 of Introductory Space Science has been hosted at The Computer UFO Network site (CUFON) since the early 1990s. Introductory Space Science – Vol. II, Chapter XXXIII: Unidentified Flying Objects
References for the 1974 Chapter 33, “The UFO Mystery”
33 - 2. Davidson, L. Flying Saucers: An Analysis of the Air Force Project Blue Book Special Report No. 14. (Third Edition). Ramsey, New Jersey: Ramsey-Wallace Corp., July 1966.
33 - 3. Edwards, F. Flying Saucers - Serious Business. New York: Bantam Press, 1966.
33 - 4. Friedman, S. “More on UFOs,” Physics Today. January 1971, 97. [Letter]
33 - 5. Fuller, J. "Flying Saucer Fiasco" Look. 14 May 1968, 58.
33 - 6. ______. The Interrupted Journey, New York: Dial Press, 1966.
33 - 7. Hall, R. (editor). The UFO Evidence. Washington, D.C.: National Investigations Committee on Aerial Phenomena, May 1964.
33 - 8. Jung, C. Flying Saucers; A Modern Myth of Things Seen in the Skies. Translated by R.F. Hull. New York: Harcourt, Brace and Company, 1959.
33 - 9. Kehoe, D. The Flying Saucer Conspiracy. New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons, 1955.
33 - 10. ____. Flying Saucers: Top Secret. New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons, 1960.
33 - 11. Lorenzen, C. The Great Flying Saucer Hoax. New York: William Frederick Press,1962.
33 - 12. Markowitz, W. "The Physics and Metaphysics of Unidentified Flying Objects," Science. 15 September 1967, 1274.
33 - 13. McDonald, J. UFOs --- Greatest Scientific Problem of Our Times? Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15219, 1967. [Paper.]
33 - 14. Menzel, D. and L. Boyd. The World of Flying Saucers: A Scientific Examination of a Major Myth of the Space Age. Garden City, New York: Doubleday, 1963.
33 - 15. Michel, A. Flying Saucers and the Straight Line Mystery. New York: Criterion Books, 1958.
33 - 16. Ruppelt, E. The Report on Unidentified Flying Objects. Garden City, New York: Doubleday, 1956.
33 - 17. Saunders, D and R. Harkins. UFOs? Yes! New York: Signet Books, 1969.
33 - 18. Stanton, L. Flying Saucers: Hoax or Reality? Princeton, New York: Belmont Books, 1966.
33 - 19. Tacker, L. Flying Saucers and the U.S. Air Force. Princeton, New Jersey: D. Van Nostrand, 1960.
33 - 20. Terry, D. "No Swamp Gas for Him, Thank You," St. Louis Dispatch, 2 June 1966, 4F. [Charles Fort article by Dickson Terry]
33 - 21. Vallee, J. Anatomy of a Phenomenon: Unidentified Objects in Space - A Scientific Appraisal. Chicago: Henry Regnery, 1965.
33 - 22. ______, J. and J. Vallee. Flying Saucers a Challenge to Science. New York: Henry Regnery, 1966.
33 - 23. Whitney, D. Flying Saucers. New York: Cowles Communications, 1967. [Look magazine special]
Donald G. Carpenter’s Published Works
1960 – Thesis, Air Force Inst. Of Tech., Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio, “Earth’s Geomagnetically Trapped Corpuscular Radiation.”
1962 – Dissertation, “Plasma Theory Applied to Ball Lightning,” Iowa State University of Science and Technology, Ph.D., 1962, Physics.
1965 – “Reactivity Approximation” American Journal of Physics 33, 961 (1965);
“Trapped Electron Component from Orbiting Reactor Neutron Decay,” Journal of Geophysical Research, V70, N23, pp. 5831-38 (Dec 1965). (With Donald A. Cohen.)
1968 – Carpenter, Donald G. “Research on Aging: A Proposal.” Science, vol. 160, no. 3828, American Association for the Advancement of Science, 1968, pp. 605–605.
Introductory Space Science was published for the 1968 Fall semester of the USAFA’s Physics 370 class.
“An Integrated Theory of Aging,” Donald G. Carpenter Ph.D., James A. Loynd M.S., Journal of the American Geriatrics Society Volume 16, Issue 12, December 1, 1968
1969 – “Biological Aging as a Diffusion Phenomenon,” Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 31, 487–504 (1969).
1969 – Analog Science Fiction, Dec. 1969, “Is Biological Aging Inevitable?” with Captain John E. Wrobel, Jr.
1972 – Environmental Space Sciences edited by Lt. Col Donald G. Carpenter, Northbrook, Ill.: Whitehall Co.
1973 science fiction novel – The Treacherous Time Machine under the pseudonym “Merlin Mesmer Merlino.” Self-published via Vantage Press, 1973.
1980 – Analog Science Fiction, Oct. 1980, Carpenter’s essay, “The Physics of Haunting.”
1982 – NASA’s Aerospace Bibliography, 7th ed., 1982, “an annotated and graded list of books and reference materials,” included Carpenter’s 1972 book, Environmental Space Sciences.
1984 – “Weighing the soul at death: Some methodological and theoretical considerations,” Theta, Journal of Psychical Research 12, 14–16.
1985 – Analog Science Fiction, May 1985, featured a letter from “Dr. Donald Gilbert Carpenter” that dealt in part with the depletion of earth’s resources.
1987 – “A possible quantum mechanical source of gigahertz noise,” Speculations in Science and Technology, 10 (1):31-36
1990 – “Electron-Spin-Reversal Noise in the Gigahertz and Terahertz Ranges as a Basis for Tired-Light Cosmology” Apeiron, No. 6, Winter 1990
1994 – “Cosmology and Quantum Mechanical Unstable States for Helium.”
Apeiron, Nr.20 October 1994, “The SRT, Quantum Mechanical Unstable States, and Cosmology” with Robert S Fritzius.
1995 – “Inconsistencies in the Derivation of the Barometric Equation.”
1998 – Physically Weighing the Soul, an e-book no longer available from 1stbooks.com.
1999 – “An Inconsistency in Sir Isaac Newton’s Derivation of the Barometric Equation,” Apeiron, 1999 Jul. – Oct. 6, Nos. 3 & 4, pp. 247- 249.
2000 – “A Compensating Term for the ‘Side Force Component’ Term in the Barometric Equation,” Apeiron, Vol. 7 Nr. 3-4, July-October, 2000.
“Replacement of the Euler Fluid and Navier-Stokes Equations,” Apeiron, Vol. 7 Nr. 3-4, July-October, 2000.
2001 – “A Simple Proof That E = mc2”, Telicom, V15, N6, pp. 26-28 (Apr 2001).
Carpenter applied for a patent for an “Energy Conversion Method” in Aug. 2001. The patent was granted in 2003.
. . .