When flying saucer inventor Otis T. Carr died September 20, 1982, he left behind business and personal papers that chronicled his efforts to get industry and the U.S. government interested in his designs for Gravity-Electrodynamic Machines to generate free energy. The collection was preserved by relatives over the years, and documents, literature, and photographs from it are presented here for the first time.
The Saucers That Time Forgot published a 3-part series, The Life and Legend of Otis T. Carr. Since then, Carr's file has been released from the FBI and his own personal papers have been shared with us. The new material required several updates and demanded the creation of a fourth and final chapter.
Part 1: The Rise of OTC Enterprises
Here’s a brief recap of the first three parts:
 |
| Otis T. Carr and Norman E. Colton from a 1958 television appearance. |
Carr was an
inventor, and he set up OTC Enterprises, Inc. in the late 1950s to market a
man-made flying saucer, the OTC-X1 circular-foil spacecraft, which was powered
by the Utron Electrical Accumulator, his free energy generator. Norman Colton
was in advertising and became Carr’s right-hand man, helping Carr raise
hundreds of thousands for the project, from saucer buffs to oil barons. The
problems began to surface with the public demonstration to prove Carr’s technology, a
launch of the unmanned OTC-X1 saucer prototype. It couldn’t fly. Afterwards,
the Securities and Exchange Commission prohibited OTC Enterprises from selling
stock, and Carr was subsequently convicted and jailed in Oklahoma for violating
state securities regulations. Carr dropped out of both the flying saucer business
and the public eye.
Yet that was not the end of his story. Little has been published about Carr’s post-conviction life or the creation of Carr Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems to generate free energy that “could be applied anywhere on this planet or in space.”
Part 4:
Otis T. Carr’s Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems
Co-author for this chapter, J.B.M., whose contributions were
invaluable.
Self-Exile from Saucers
The surviving files of Otis T. Carr contain little from the OTC
Enterprises, Inc. days. When Carr was facing charges in court, he fled Apple Valley,
California for Vashon, Washington, leaving behind most of his papers and
mementos. About all that remained in his possession from that era were a few publicity
photos, copies of his 1957 Atoms for Peace brochure, and some newspaper
clippings. Carr was released from his Oklahoma jail sentence on January 17,
1962, and the collection documents that period up until his 1982 death, with
correspondence, invoices, bills, patent applications, legal papers,
photographs, and more.
Otis T. Carr and Eleanor lived for a while in Baltimore after his
jail term. There was some bad blood between Otis and some of his former OTC
Enterprises associates there, and he wanted nothing further to do with them.
Carr severed his ties to the flying saucer business, the OTC-X1 project, his
spaceship ride, and his loving UFO fans. Before all his troubles started, Carr
had found friends and investors in and around Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, so Otis
and his wife moved there. Perhaps with the support of Eleanor, Carr was in
better control of his alcoholism. The relocation gave him a fresh start,
and it wasn’t long before he began developing a new free energy enterprise,
this time as a more legitimate business.
All Carr kept from the old days were some of his business
relationships. In 1963 he renewed his relationship with two attorneys in
Oklahoma: Hubert A. Gibson as his general counsel and Jerry J. Dunlap as his
patent lawyer, responsible for registering his inventions, copyrights, and
trademarks. Carr reconnected with a few of his old investors in the United
States and Canada who had paid to become exclusive regional distributors for
OTC Enterprises. The first was Alex Andreotta of New York, who entered a
contract with “Otis T. Carr, individual” for the production, development, and
distribution of a “power gain device.” Money from old and new investors
provided the means to construct a working model to demonstrate the principles
of his free energy technology.
1963: The Demonstration
On Nov. 23, 1963, at R. H. Dreshman & Sons, Inc. in Homestead,
PA (Manufacturers of Special Machines), Carr held a demonstration of his power
gain technology, attended by five witnesses. One was Milton Palkowitz, an
electrical engineer at the Panelcraft Company of America (McKeesport, PA) who
later wrote a letter testifying to the successful operation of the machine,
“which has heretofore been considered impossible by known engineering science.”
 |
| An early Power Gain Machine wooden-framed prototype |
Afterwards, Carr and the witnesses each signed a notarized statement that “a machine invented by Mr. O.T. Carr has been successfully recycled by its own power and it has been witnessed by the following persons:”
 |
| Otis T. Carr, Milton Palkowitz, Panelcraft, Inc., Matthew S. George, Panelcraft, Inc., Robert Ray Davis, Walter Dressel, Machinist, and Roy E. Dreshman, Treas. |
The notarized statement and Palkowitz‘s testimonial letter became the centerpiece for Carr, used to establish the credibility for his concepts and products when meeting with potential customers or investors.
Carr Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems
Otis incorporated Carr Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems in
Pennsylvania on May 7, 1964, and later in Canada, as “Carr
Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems, Ltd.” Carr leased an industrial building from
Thomas Wilson at 401-403 Wide Drive, McKeesport, Pennsylvania, then purchased
equipment and supplies for a machine shop to fabricate a prototype of his
invention. The trademark for the company was a hummingbird, and he put its
colorful image on the company sign and literature, part of his marketing plan
developed to reach potential customers.
Carr also put together a team of executives, office staff, electrical engineers, and mechanics, including three of the participants from the 1963 demonstration. Joining Carr as CG-ES executives were inventor Dante Donatelli as Vice President, and for Secretary and Director, Michael A. Lukish, who had recently retired from government service. Unlike the participants and investors in his previous enterprise, none had known ties to the flying saucer scene. Below is the company roll circa 1965, with their position, if known:
Otis T. Carr, President; Dante A. Donatelli, Jr, Vice President;
Michael A. Lukish, Secretary and Director; Virginia G. Bach, Administrative
Secretary; Nancy L. Donatelli, Administrative Secretary; Milton Palkowitz,
Electrical engineer; Matthew S. George, Electrical engineer; Walter Dressel,
Machinist; Albert W. Eckels, Night watchman. Also, Curtis O. Herbert, Robert P.
Mains, Howard W. Ransick, Sr, Louis G. Vitsas, and Louis Volpato.
 |
| Tentatively identified as: Milton Palkowitz, Michael A. Lukish, Otis T. Carr, and Dante A. Donatelli, Jr. |
Over the next several months, the company was busy with getting set up and constructing the metal frame and components for the power gain machine. Otis was also at work inventing, refining designs, developing an elaborate marketing plan, and preparing patent applications. Capitalization was always a problem, and Carr claimed project delays were due to cash flow problems caused by “a breach of contract by my financial associates in Canada,” (possibly Robert P. Young of New Brunswick, Canada, a former OTC financier). Some relief came on May 25, 1964, with Carr’s second contract. It was with D. Daniel Martella and Frank Santora (another old OTC investor) for exclusive distribution rights for the power gain device in Delaware.
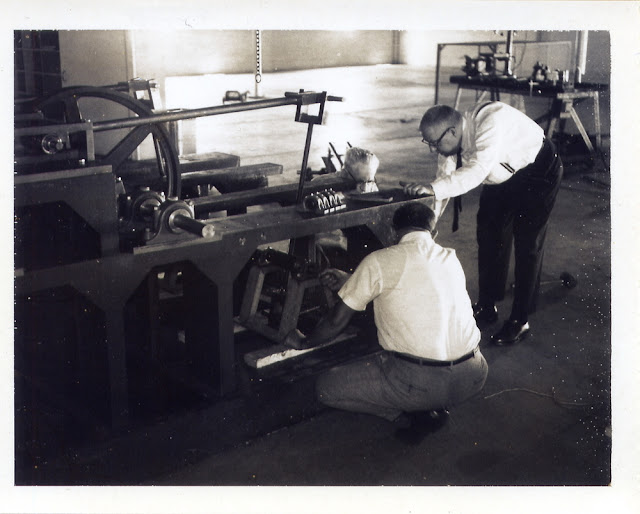 |
| Carr and his team working on the Power Gain Machine |
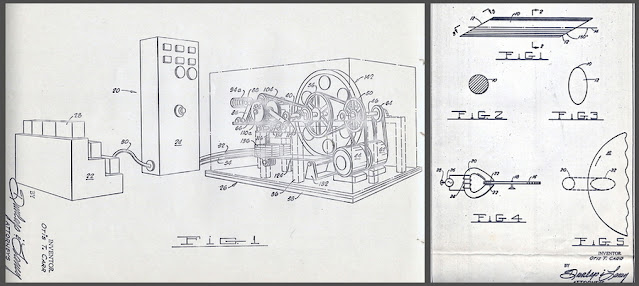
Carr wrote to his patent counsel Jerry Dunlap on Aug. 27, 1964, about construction of “Big Joe,” capable of power gain electrical energy transfer, “a true 4th dimensional machine.” The correspondence provides the best insight on how the power gain machine was supposed to work. Carr explained that electrical energy transfer was produced by two flywheels and a dimension bar magnet, and said, “The lines of force 180° apart are crossed dimensionally in the field rather than physically.” On Carr’s behalf, Dunlap filed applications for two patents: one for the device (“Power Gain Device,” serial number 418,952, on Dec. 14, 1964) and one for perhaps its key component (“Shaped Magnet,” serial number 397,526, on Sept.18, 1964). It’s interesting to note in the patent drawings and surviving photographs of prototypes, there’s no trace of the “Utron Electric Accumulator” that was crucial to his free energy designs from before.
Jerry Dunlap also helped Carr pursue two Canadian investors. They gained an ally in Mr. John Dolan, and later approached New Brunswick attorney Hendry O. McLellan about financial support for CG-ES of Canada. Patents for the products were also applied for in Canada.
Like Carr had done in 1957 with OTC Enterprises, CG-ES was presented as a real business. Carr established a company with a building, staff, and manufacturing crew, and even held corporate board meetings with officers and provided employee insurance policies. During the OTC Enterprises days there was an income stream from the sales of books and model plans, but Carr’s new company had no other products or services besides the power gain concept. Carr Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems needed sales. By mid-1965, Carr was confident enough in the business that he debuted the company to the public.
Carr’s full-page advertisement was published in McKeesport Daily News (PA), June 5, 1965, “Free Energy Comes to the Planet Earth.” It advertised “Perpetual Energy-Motion Machines,” and included a photo of its building, which carried the name, “Carr Gravity Electrodynamic Systems,” and the facility’s purpose: “Research - Development - Manufacturing – Marketing.” Using the same imagery, Carr printed a four-page “Free Energy” brochure on June 28, 1965, featuring a full color picture of his hummingbird trademark on the cover.
Issuing Stock
The finances were not improving. Shortly after he incorporated
CG-ES, Carr obtained a certified copy of the 1959 court document, the SEC’s “Permanent
Injunction” forbidding OTC Enterprises to issue stock. CG-ES was a different
entity, so in the first quarter of 1966, the company began issuing shares at
$10 per share. Periodic shareholder meetings were conducted, assuring investors
the company was making progress. Over $150,000 in shares were issued, raising
cash from investors, and used as payment of debt to creditors, including at
least three former OTC Enterprises, Inc. regional distributors. Still, the
company continued to sink further into debt. They needed a big sale.
Petitioning the President
In 1957, Carr had managed to obtain a meeting with the US government to pitch
the OTC Enterprises saucer for $20,000,000. His proposal was rejected, but he was
going to try them again, but with a more affordable project, his power gain technology. Carr sent a letter to President Lyndon Johnson on Aug. 23, 1965, with an angle
that he thought might get the government interested, “the water crisis on the
Eastern Seaboard.” He enclosed the CG-ES brochure and proposed to use his
technology to power a water desalination plant. Carr also sent copies to “the
five Governors on your Committee and to the Secretary of the
Interior.”
 |
| Sec. of the Interior Stewart Udall and President Lyndon B. Johnson |
That copy of the water desalination proposal letter to Governor William Scranton prompted a reply from the Pennsylvania Director of Research & Development, David R. Maneval, Ph.D. They subsequently met, and Maneval was apparently interested in Carr’s technology.
Meanwhile a cautious response came from the U.S. Department of
Interior, and in the exchanges, the officials requested factual evidence of the
performance of the machine. Carr offered his “Power Gain Device” patent
application to lend credibility to his invention, but the Interior wanted
something more substantial. On Feb. 9, 1966, Carr wrote to Robert W. Nelson,
Deputy Asst. Secretary, that he would provide certified performance reports
from an engineer as soon as they were complete. David R. Maneval’s Ph.D. was in
mineral preparation from Pennsylvania State University. He was either intrigued
or sympathetic enough that he wrote letters in Spring 1966 to two companies in
Pennsylvania suggesting that they consider Carr’s machine ideas. Apparently at
Otis’ request, Maneval also wrote a letter endorsing Carr to the U.S.
Department of Interior’s Robert W. Nelson.
Carr continued to send out CG-ES sales literature far and wide. On
June 2, 1966, John. R. Pegan, patent counsel for Pittsburgh’s Crucible Steel,
wrote a rejection letter saying the company had “no interest in pursuing the
subject matter…” Without flying saucers and Norman Colton’s promotion, Carr’s
new venture struggled. The plan must have been for advertising and brochures to
bring in orders, but that didn’t happen, and unpaid bills began piling up from
day one. Invoices show that Carr Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems was thousands
of dollars in debt. Beginning in 1965, several of the companies involved took
their cases to court, and in a few instances, CG-ES property was liquidated in
Constable’s Sales to pay creditors.
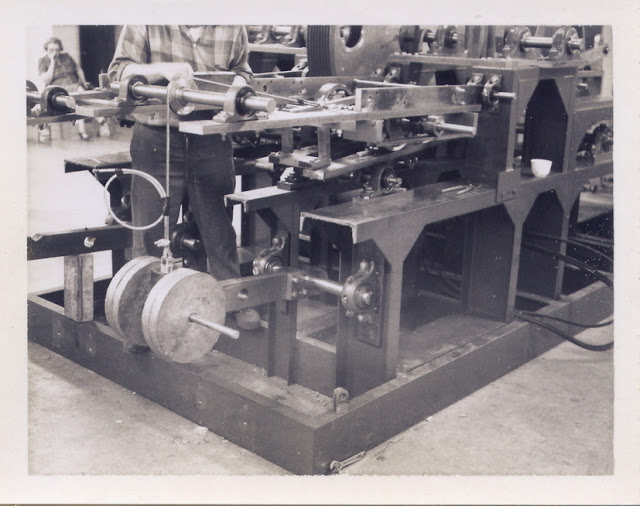 |
| The CG-ES machine |
In the fall of 1966, Carr was forced to close the CG-ES plant. He wanted Eugene Carini (his old OTC-X1 saucer technical advisor) to come from Connecticut to rescue the shop machinery. Instead, on October 13, 1966, much of the equipment was surrendered to his plant landlord to terminate the lease and pay back rent. That was not the end of CG-ES, though, as it still existed on paper. Some of the remaining equipment and models were put in storage in the basement of Dante Donatelli, leased at the price of $50 per month. Carr continued to promote the product, using his home at Royal York Apartments, 3955 Bigelow Blvd, Pittsburgh, PA, as the address for CG-ES. The company may have been Carr’s sole source of income, and he was unwilling to let it go.
Mr. Carr Goes to Washington
Within weeks of shutting down the company building, Carr headed to Washington, D.C. He set up at the Statler-Hilton hotel for three weeks (from about Nov. 21 to Dec. 14, 1966) launching a letter writing campaign to promote the CG-ES machine. His targets included the Department of Interior, Defense Secretary Robert S. McNamara, President Johnson, and private companies.
 |
| Justice William O. Douglas of the U.S. Supreme Court. |
The letter campaign began paying off with a prior contact Otis had met years before in relation to a Maryland nature conservation project, and he played on that angle. Carr wrote to Supreme Court Justice William O. Douglas, who agreed to meet with him in Nov. 1966. There is no record of that conference, but within two months, Carr and some of his CG-ES staff were granted a meeting with the Department of Interior about his water desalination proposal. It took place at the Continental conference room at the Statler Hilton on Saturday, January 5, 1967.
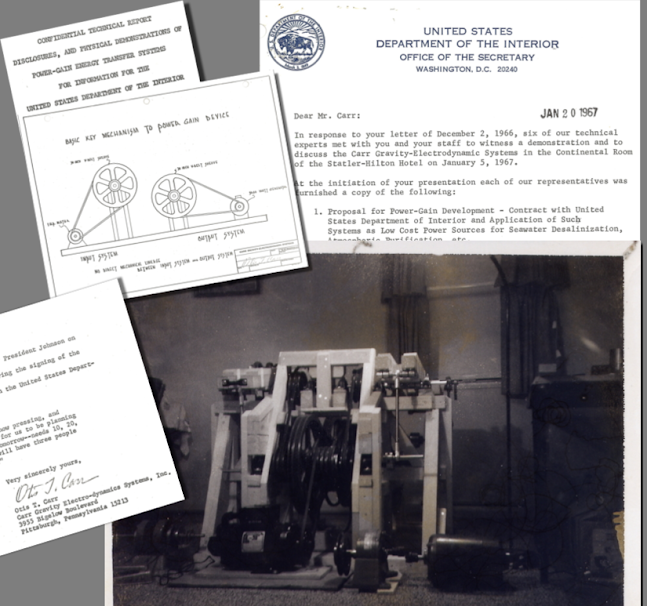 |
| The half-scale wooden-framed power gain machine model. |
The Interior sent six of their technical experts to hear Carr’s proposal, which sought financing of $500,000 to develop “Power-Gain Energy Transfer Systems.” Carr’s presentation included a reading of two papers, the first was “Proposal for Power-Gain Development…,” but there was nothing detailing water desalination; he just touted his technology as a revolutionary energy source. His other paper, “Confidential Technical Report Disclosures…” opened with Carr’s three-page biography of his scientific accomplishments, including the story of his training by Nikola Tesla. There was no mention of the OTC-X1 project or his criminal conviction, however. The meeting culminated with Carr showing a color film of the operation of the first full-scale working model of his machine, then presenting a half-scale wooden model to point out the principles that “could be applied anywhere on this planet or in space for Power-Gain Energy Transfer.” Carr closed by saying that he’d be leaving town on Tuesday and, “I will expect an answer by that time.”
What he got instead was a polite rejection letter from the
Interior, stating, “It is the unanimous opinion of our experts that the
material presented during your demonstration is not sufficiently substantive…
We cannot visualize your new principles in light of our knowledge of the
fundamental laws of the conservation of energy or motion.” That was Carr’s big
shot, and he must have been as profoundly disappointed in this rejection as in
the 1959 saucer launch failure. Correspondence shows he felt discouraged by the
“pressure of money lack and the environment of incredulity,” and bitter towards
the government and the scientific establishment for rejecting his inventions.
The X1-Files, 1966: Lear Jet Aircraft and Saucer News
Before leaving 1966, let’s back up for a brief episode involving
the topic of flying saucers.
After his jail term, Carr avoided the press and any mention of
flying saucers, but there was one exception. Due to a current wave of
sightings, on April 2, 1966, The Daily Oklahoman published reporter
Katherine Hatch’s interview of Carr by telephone “For the past two years, Carr
said he has been doing research on an electrified magnetically propelled engine…and
he has made a proposal to the government...” CG-ES was not named, but
describing his device, Carr said, “It’s a gravity motor. I have been successful
in my research and have built a machine that creates more energy than it uses.”
On the topic of flying saucers, Carr said his spaceship OTC-X1 launch was a
flop because he "never had a chance to finish,” and blamed it on
insufficient funding. He thought the recent UFO sightings were proof that his
work was valid. “I don’t say the craft are from somewhere else. I have proved
in laboratory experiments that you can levitate a body electrically. ...it’s
ridiculous in my mind, to pass it all off.”
 |
| The Daily Oklahoman, April 2, 1966 |
Later that year, saucers were still on his mind. On Nov. 23, 1966, while in Washington, D.C,. Otis T. Carr wrote a letter to the President of the Lear Jet Corporation, William P. Lear, Sr.
 |
| William Lear with his arm around son, John Lear. |
He provided Lear with a brag disguised as an update. In April and May, Carr had mailed him the CG-ES brochure and asked for the company to invest. Engineer Samuel H. Auld, head of Lear’s Electronics Division came to Pittsburgh and met with Carr, but ultimately declined the proposal. Carr told Lear that another backer had been found, and that he had completed the prototype for the Power Gain Energy Transfer machine, and he was now talking with the U.S. government to implement the technology.
Finally, Carr got to the real reason for writing, requesting a
meeting with Lear on a matter of shared interest, saucer flight. Bill Lear was
a UFO witness in the mid-1950s and had become a public advocate of flying
saucer and antigravity research. Otis said his energy project kept him from pursuing
the OTC-X1, but he encouraged Lear to pick up the work to become “the first to
build, test and fly an electrically powered circular aircraft similar to the
controversial U.F.O.”
 |
| Thanks to Lance Moody for the illustration |
Whether Lear replied or not is unknown, but it’s interesting trivia that Bill’s son John Lear went on to become a UFO personality, spreading rumors that later became X-Files plots, and helped bring us Bob Lazar and the tales of aliens and flying saucers being stored at Nevada’s top-secret base, Area 51.
More significantly, Carr’s letter to Lear (along with the Daily Oklahoman article) can be read as a confession. No matter what his fans might want to believe, Otis himself was never able to get a saucer to fly.
Splits, Debts and Stock
In the aftermath of the disappointment in Washington, DC, one of Carr’s key supporters not only had a loss of faith, but his heart had also turned. Michael A. Lukish had joined the company after retiring from government work, and it looks like he was a straight arrow, possibly serving as the company’s moral compass. Lukish sent a letter resigning as Secretary and Director of CG-ES on July 2, 1967. Over the following months, other letters followed, about what he viewed as Carr’s fraudulent presentation to the Department of Interior. He’d had an independent electrical engineer evaluate the data and concluded the 1963 test was “incomplete, inadequate, inconclusive, and invalid.”
On Dec. 6, 1967, Lukish’s letter vehemently condemned Carr’s machine as fraudulent and said,
“you never had and do not now have a power gain machine…All of the people who have advanced funds to you, over two hundred and twenty-five thousand dollars since 1962, in support of you and your wife, and your technology… were misled. In addition, since 1962 you have over sixty thousand dollars of unpaid cash advances to you and your corporation, O.T.C. Enterprises Inc., and unpaid debts in Baltimore, Md, Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, and Apple Valley, California.”
He enclosed a copy of a letter from Milton Palkowitz disavowing the 1963 test
results and his endorsement. Lukish demanded Carr cease using that material or
he’d report Carr to the local and national authorities, including the S.E.C.
and the F.B.I. Otis compromised, writing that he would attach Palkowitz’s
disavowal letter to any future submissions of the 1963 validation document.
That may have satisfied Lukish since there’s no record of any law enforcement
agencies responding to his complaints. With the 1963 validation document no
longer usable, Carr conveniently came up with a replacement on March 20, 1968.
The new certification document was handwritten, signed only by Carr and Donatelli.
 |
| Carr’s attorney said not to worry about the typo in the company name. |
On Feb. 13, 1968, Carr formally changed the company’s address to that of his apartment. Carr’s solution to the money problem was to offer more stock. To do it lawfully, he sought new legal counsel. On April 5, 1968, Washington, D.C., attorney George Leonard advised Carr that legal loopholes allowed it, but he must not publish a prospectus or solicit the shares outside of Pennsylvania. Also, recipients were required to sign a disclaimer acknowledging that the stock was speculative and CG-ES’ technology was “scientifically improbable.” Like the new validation document, Carr created the new shares out of thin air. Carr himself determined the valuation of the company, and the initial stock certificates were homemade and handwritten, signed by Carr and witnessed by Donatelli. In time, he had formal stock certificates printed, and began issuing them to investors and creditors, stating that they were “unregistered, non-transferable stock of Carr Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems Inc. at the introductory par value of $0.05 per share in a capitalization of 6,000,000 shares.”
Many of Carr’s investors were not wealthy people, and the money they had invested would have been a significant portion of their life savings. As for the creditors, since the chances of getting their cash refunded was zero, taking the stock certificates was better than nothing. The shares issued in 1968 totaled 4,672,296. Carr had apparently begun CG-ES with the best of intentions, but as it floundered, he resorted to the same kind of financial hustles that ultimately killed OTC Enterprises.
1970: The AX-1 Interdimensional Perpetual Free Power Machine
 |
| Link to PDF of the two letters and the brochure: Carr Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems Inc. |
Carr received some interest from the Kentucky Rural Electric
Co-op, who sought additional data to satisfy their staff. Carr replied with his
usual supporting data and a sample contract. It didn’t pan out.
Edith Nicolaisen of Sweden was the founder of the Parthenon,
publisher of the 1959 translation of Carr’s Atoms For Peace. On Nov. 16,
1970, he sent Nicolaisen a letter hoping she would become his first customer
for the AX-1. It revealed his thoughts and frustrations, and it also contained
some rare comments from him on extraterrestrials. Quoted in part:
“During the past three months I have mailed more than 100 of the brochures to Agencies of the U.S. government, Leading Manufacturers and the Energy Field and Celebrated Individuals who claim they are interested in Humanity's welfare. Not a one has responded.
The cruel dictatorship that rules this planet with an iron fist is afraid to challenge me, one poor, lone, weak individual!
In their mad quest to maintain their murderous dynasty wherein they will gladly trade a gallon of blood for a barrel of oil they still, with all their powers, are afraid of Free Energy and Free Power.
It was only through divine guidance that I conceived of the plan expressed in the brochure, payment 90 days in advance, This is my protection – it also separates the sheep from the goats and puts an end to hypocrisy.
The way to become associated with me is to buy a machine, when 300 of these machines are in 300 different places performing it will be impossible for the news not to become known and the ‘New Age’ will be here.
Inter-planetary beings will never make themselves known to earth beings so long as we exalt murder as a way of life.
If you and those whom you know can get together the money to buy the first AX-1 please forward the same and I will fulfill my end of the bargain.
Very sincerely and best regards,
Otis T. Carr”
The offer was not accepted.
Carr tried the US president again, this time, sending a telegram to Richard M. Nixon at his home in Key Biscayne, aka the “Florida White House.” While there’s no record of a reply, Carr did receive responses from the brochures and solicitations sent to others. Carr heard back from the New York Times, television host Art Linkletter, W. W. Grainger, Inc., the Sierra Club, and the United Nations.
Further Experiments and Reconnecting with Saucer Supporters
Eugene Carini was an inventor and an early Carr supporter,
investing $10,000 to become a regional exclusive distributor, OTC
Enterprises of New England. In the mid-60s, Carini created Energy Systems,
Inc., to develop electric cars and continued that work after he retired and
moved to Vero Beach, Florida.
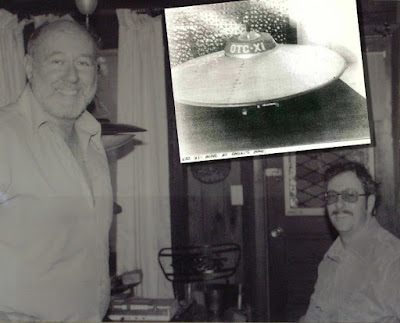 |
| Gene Carini circa 1970 with Jim Murray. |
Carini had a “cooling off period” after the Frontier City saucer fiasco, but reconnected in 1971, when Gene wrote Carr with a plan he hoped would re-motivate and revitalize Otis’ spirit and productivity. Carini offered to pay for Carr’s travel to Vero Beach and help finance the materials to continue the free energy research. Carr accepted and made the trip in early March from Pittsburgh to Florida. Together, they built some models of the AX-1 that Carini said showed promise but needed “modifications.” After three weeks, Carr went back home and that was the last Carini saw of Otis T. Carr. Carini continued the work, essentially substituting for the CG-ES machine shop, and again the bills were rolling in. On June 20, 1971, Carini wrote to Carr that “Bill and Lou are screaming for their money.” Carini said, “the AX-1 is working,” but that a demonstration was needed to convince people and “end the money harassment. …my property is now in jeopardy due to my participation in the construction of the AX-1.” On Jan. 20, 1972, Carini wrote to Carr about coming back for another visit to continue the work, but for some reason, Otis declined. Interestingly, Otis failed to secure any power gain machine patents, but in the 1970s, Carini was able to patent four Carr-style inventions featuring similar principles like counter-rotating flywheels.
 |
| Eugene P. Carini from his 2001 interview with Lance Moody. |
About the same time Carini reconnected with Carr, Otis mailed his AX-1 brochure to George Emerson Fox, a ufologist in New York City. Fox took an interest and began contacting Carr’s old friends in the flying saucer world, sharing Otis’ address with them, which led to some interesting exchanges. Contactee Carl Anderson also wrote, saying he loved Carr “like a father” and wanted to renew their friendship. When Carr replied months later, he enclosed a brochure for the AX-1 asking if he knew anyone who might like to buy one.
Dorothy S. Sawyer wrote a loving letter to Carr, and it included details of her own sad story. Back in 1961, Dorothy was working in a California hospital. She traveled to Apple Valley and met Otis, his wife and OTC associates. She said, “Dennis Rapolti and I were western representatives for the OTC X1 project.” She believed in the cause and began investing in it and, “Later the name was changed to the ‘Millennium Agency.’” When Norman Colton and company were in from Baltimore, she provided them lodging. After everything folded, Dorothy was crushed by the loss of her investments and left $5,000 in debt. “I almost had a nervous breakdown and lost job after job.” She had to “keep finding new jobs and paying back money… my family couldn’t accept any of this.” Dorothy’s husband divorced her, and she moved away from her children. Despite it ruining her life, she still regarded Carr fondly. “God bless you Otis, in your work…”
Carr replied to Dorothy Sawyer on May 14, 1972, but had
nothing to say about her hardships, instead he complained of declining health
and having to survive on a Social Security check of $100 per month. He seemed
to blame her troubles on his old partners in OTC Enterprises, saying, “I have
not seen Dennis Rapolti since I saw you both on the Desert more than 12 years
ago. The same goes for Norman Colton. I had no part in their activities and no
desire to renew anything with them.” Furthermore, “Many people whom I trusted
have tried to destroy me… It would take a book to tell all the things… it is
better left unsaid.” He sent her a copy of the AX-1 brochure, in the hopes that
she might know “someone with sufficient funds to buy one of my machines under
the conditions specified.”
The File Ends
There wasn’t much left of CG-ES by 1972, but Dante A. Donatelli,
Jr was still involved, and he received a letter forwarded by their patent
attorney. Jerry Dunlap had helped to arrange for two Ph.D. candidates in
mechanical engineering at Oklahoma State University to examine the AX-1 plans.
This could have provided the scientific validation Carr had long sought, but
unfortunately for Otis, they concluded: “Our evaluation of Mr. Carr’s
Power-gain Energy Transfer Machine reveals that it cannot work…” In perhaps
unrelated matters, 1972 marked the end of Dunlap’s association with Otis Carr.
Later that year, Carr devised a plan to bring Free Power to all the nations of the Planet Earth. An aborted package addressed to the Ambassador to Canada at the United Nations dated Dec. 27, 1972, contained a letter of introduction and the AX-1 sales brochure from 1970. Carr’s plan was to send similar packages to every nation’s ambassador to the U.N., but there’s nothing to show if he followed through. Carr Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems escaped reprisals from investors or penalties from the SEC or law enforcement. It just faded away.
Not much is known about Carr’s activities after that. In 1973 Gene Carini wrote requesting he send the final designs on the “PM Model,” and Gene continued to write to him until 1974, when Otis stopped responding. About the same time, Otis and Eleanor relocated to an apartment in a retirement community, East Hills High-Rise, 2360 Bracey Drive, Pittsburgh. After the move, Otis occasionally received some mail from saucer fans, but he seldom replied. In a letter to a friend, his wife Eleanor later described this period, “Due to his ill health and lack of finances, Otis had been very inactive for the past ten years.”
The Final Saucer Consultation and Chance for Fame
Carr’s last known saucer business was mentioned in Douglas Curran’s 1985 book, In Advance of the Landing. In the 1960s, Warren Goetz led a group with similar saucer-building plans, and frustrated by the lack of progress, one of his partners “sought out the ailing Otis T. Carr” for some technical guidance in 1977. That passage seems to be based on the experience of Jim Murray, an electrical engineer and inventor, so we contacted him for the story. Murray told us that with a hint from Gene Carini and some detective work, he was able to locate Carr, then flew from Newark with a friend to visit Otis at his apartment in Pittsburgh. While Eleanor may have been less happy to see them, Otis entertained them for twelve hours with romanticized tales of his life and work. Jim was particularly interested in hearing what Carr had learned from Nikola Tesla but was left uncertain if the two had ever met. While Murray thought Carr’s concepts had potential, he “didn't know beans about science and technology.” As for helping with the saucer, Carr said that in 1960 at the Apple Valley plant, someone broke in and stole his blue notebook with the OTC-X1 plans. The secret wasn’t completely lost however, Otis said the working principles of his flight technology were contained in his 1959 saucer amusement ride patent. Jim Murray had hoped to consult with Carr for advanced scientific principles, but instead got mostly “double-talk and gibberish.”
Together Forever
Otis T. Carr spent the rest of his days living quietly with Eleanor in Pittsburgh, but suffered from health problems. At some point he became seriously ill, and Otis T. Carr died in the hospital on Sept. 20, 1982, at the age of 77. The cause of death was pneumonia and renal failure. Eleanor Mathews Carr died at the age of 89 on February 4, 1994. She was buried beside Otis at Allegheny Cemetery in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
 |
| Pittsburgh Press, Sept. 21,1982 |
 |
| Photo of Otis and Eleanor from 1966 in Maryland. Provided by J.B.M. |
Epilogue: Taking Stock of the OTC Story
Due to him avoiding publicity, details of Otis T. Carr’s later years were virtually unknown until now, and all he is remembered for is the free energy spaceship flop. What’s most interesting about that episode is not so much his failed saucer, but how and why people believed in the man behind it. Carr made his public debut in late 1957, but months earlier, Harold J. Berney had been arrested by the FBI for saucer-related fraud. Reinhold O. Schmidt also got his start in 1957, and he was eventually convicted in 1961 for two counts of saucer-related grand theft. The three saucer swindlers had much in common. Berney, Schmidt and Carr all collected money from investors in saucer schemes, all involved an element of free energy, and all were convicted for their crimes. Each of them, especially Carr, capitalized on the intersection of saucer belief and the dawning of the space age.
. . .
What happened to...?
Norman Evans Colton left the saucer life, abruptly abandoning the Millennium Agency
and dropping out of sight in 1961. He eventually moved to Pennsylvania and
reportedly ran a florist shop, and Otis never heard from him again. Colton was
last mentioned in contemporary literature by Paris Flammonde in his 1971 book, The
Age of Flying Saucers: Notes on a Projected History of Unidentified Flying
Objects. Flammonde said that many people believe Norman E. Colton “to be
the inventor of Otis T. Carr.” Colton died on July 29, 1997, at the age of 83.
Mrs. Hildegarde Wheeler Shea left when Carr’s Baltimore office closed and
became a partner in a wildlife park where OTC associate Dennis Rapolti worked
for her. She died following an illness on April 20, 1966, at the age of 40.
Wilfred C. “Bud” Gosnell returned to his old job in the dairy industry until his retirement. He died in Baltimore at the age of 65 in June 1967.
Eugene P. Carini continued inventing, and he patented several devices into the 1970s. However, there’s no record of his success with a free energy device or a flying saucer. He died in Florida on July 13, 2003, at the age of 81.
Wayne S. Aho continued to lecture on UFOs, but his message became increasingly more religious in tone, with a heavy dose of Biblical prophecy. In Oct. 1960, he was elected to the board of directors of Daniel Fry’s Understanding, Inc. His Washington Saucer Intelligence “organization” faded away, but in 1963, Aho created something else for himself to be director of, the New Age Foundation, which held annual spiritually-themed seminars for decades at Mt. Rainer, the holy location of Kenneth Arnold’s famous 1947 saucer sighting. He died Jan. 16, 2006, at the age of 89.
Dante A. Donatelli, Jr. , vice president of Carr Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems moved to
Texas and went on to offer his own free energy products in 2005, online as
OneGift4Power.
The Frontier City OTC-X1 ride? In 1960, a bigger and better-known saucer opened in New York, the Braniff "Space Ship" at Freedomland. There was no documentation found for when the OTC-X1 attraction was shut down, but no advertisements for Otis T. Carr’s spaceship ride at Frontier City were found after 1961.
. . .
Television Trivia
Otis T. Carr received a lot of media attention in his lifetime, almost all of it in connection with his saucer enterprises. He appeared several times on local news programs, but national television coverage eluded him. A fictional version of Otis T. Carr was featured in the March 19, 1978 episode of NBC’s Project U.F.O. In the secondary storyline of “The Howard Crossing Incident” (written by Donald L. Gold and Lester Wm. Berke), the Air Force received a report from Mrs. Marshall, who was concerned that her husband had made a bad investment of $10,000 stock in Advanced Aerodynamics Corp., a flying saucer factory. There, owner Darryl Cochran had shown the Marshalls a craft under construction, saying it was powered by an anti-matter energy engine, and their investment would be worth millions when it launched in six months. The Air Force investigators exposed Cochran as a swindler, his saucer nothing but a prop from an old science fiction movie. Like in the real Carr story, the customer refused to face facts. Mr. Marshall was livid that the saucer hadn’t been given a chance to fly and told them, “I could have made a fortune on that stock if you hadn’t butted in.”
 |
| Project U.F.O. episode, The Howard Crossing Incident |
Television apparently wanted the real Otis T. Carr story, too.
George Emerson Fox wrote Carr on April 20, 1982, saying that he had gotten the
NBC show Real People interested in the OTC story. Since getting out of
jail in 1962, Carr avoided the press. Nothing came of it. Carr died later that
year, but not everyone got the word of Otis’ passing, and his story was still a
topic of interest.
Dorothy Holdridge of Toledo, Ohio, wrote to Otis and Eleanor Carr on May 11, 1983. She had been contacted by Walter H. Bowart (author of the 1978 book, Operation Mind Control) who wanted to write about Carr’s life story, possibly for a movie. She’d heard from Bowart that, “all your papers etc. were found in… Apple Valley… in a dusty dirty garage for all these years. I could have cried. Bowart said you are a man of vision… This may be a turning point for you…” She had also heard from George Fox that, “Mike Wallace (of 60 Minutes) is trying to locate you.” There’s no further documentation, but it looks like the CBS show was interested. According to family lore, 60 Minutes approached Mrs. Carr after Otis died, but Eleanor flatly refused them.
. . .
For Further Reading
The Otis T. Carr Files
Documents, literature, and photographs from the papers of the estate of Otis T. Carr, mostly from 1964 - 1972.
PDF of 92 pages: The Otis T. Carr Files
FBI Files
The FBI opened a file on Wayne S. Aho when it received a citizen’s letter warning that he might be impersonating a military officer. Aho might have exploited his status as a retired Army intelligence officer, but that alone was not a criminal offense for them to pursue. The FBI dossier on Wayne Aho also contains many documents from Otis T. Carr’s file.
Collection of Carr’s letter and Space-O-Gram announcements about the 1959 Frontier City “Demo Day” for OTC-X1, including correspondence about it from Canadian ufologist Wilbert B. Smith. OTC-X1 Documents
“Otis T. Carr and Dimensions of Mystery” is a Facebook page that features many newspaper clippings, photos, and other items.
“Otis T. Carr: Utron” is a crackpot web page with some coverage of the Carr story, featuring transcripts of some period newsletters, articles and interviews.
“Contactees, Cults and Cultures” by David Stupple & William McNeece, 1979 MUFON UFO Symposium Proceedings pp. 46-61, tells the story of Warren Goetz (whom they call “Gordon’), who was inspired by Otis T. Carr’s efforts and later formed the cult, “The Institute for Cosmic Research” and tried to build their own flying saucer, the Bluebird. Video of the fate of the Bluebird, circa 1995.
Lance Moody, as part of a planned OTC Enterprises film project, interviewed James W. Moseley of Saucer News and Saucer Smear in 2001. While Moseley didn’t have anything to say about Carr himself, he briefly discussed his cohort Wayne Aho. More importantly, Jim talked about Long John Nebel and his radio show, providing some backstage details and insight into Nebel and his involvement with ufology. See the video at Jim Moseley, Journal Subscriber, 1931-2012.
Lance Moody presented a lecture on his investigation, “Daylight Disk: The Otis T. Carr Story,” summarized by Bob Streifthau in Cincinnati Skeptic, April/May 2003.
Way Out World, 1961, by Long John Nebel has a chapter on Carr, "The $20,000,00 Ticket to the Moon Plus Some Impossible Inventions."
. . .
After the original publication of this article, an extended member of Otis. T. Carr's family, J.B.M., wrote with numerous comments, corrections, correspondence and photographs that have greatly helped in revising this work. He provided almost all of the material on Carr Gravity-Electrodynamic Systems and collaborated with us on the fourth chapter.
A special thank you to Lance Moody, whose research informed much of this examination. In 2001 he began conducting interviews for a proposed documentary on the OTC story and spoke with six key participants in the OTC story, Eugene Carini, Ellery Lanier, Wayne Aho, Gurney G. Warnberg, Ralph Ring and Dennis Rapolti. Details from those conversations were invaluable. Lance also furnished another key reference used to recreate the Carr timeline, the outstanding article by Richard Gehman from True magazine, Jan. 1961, "King of the Non-Flying Saucers,” as well as scans of the notebooks that Gehman made while researching it. Lance also provided the title art for this project.
Also, thanks to:
Louis Taylor of Information Dispersal for several original Carr documents and photos.
Isaac Koi for help in tracking down early flying saucer magazines and for his contribution in archiving them with the AFU, the Archives for the Unexplained.
David Houchin of the Gray Barker UFO Collection at the Clarksburg-Harrison Public Library, Clarksburg, WV, for documents on Norman Colton. Håkan Blomqvist of the AFU for sharing rare documents, including Carr's 1970 correspondence. Håkan Blomqvist´s blog.
Jim Murray for sharing the details of his 1970s conversation with Otis T. Carr. The Fringe Energy: Alternative Engineering Resources profile of Jim Murray.